Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Training
Trusted by 20,000+ professionals across India, the US, and Middle East.
About Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Training
At UnoGeeks, our Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Training is designed to make you project-ready and placement-focused from day one. With enterprises rapidly migrating databases, applications, and workloads to Oracle Cloud, the demand for skilled OCI Cloud Engineers and Architects specialising in Compute, Networking, Storage, Security, Identity & Access Management, and High-Availability cloud architectures is at an all-time high.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure professionals today command strong salary packages, with freshers securing competitive entry-level roles and experienced consultants earning high-paying positions in top consulting firms and MNCs. Our training goes beyond theory with real-time projects, hands-on infrastructure deployment, interview preparation, and live scenario-based learning to make you fully job-ready.
By the end of the program, you won’t just understand Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Skills — you’ll be ready to crack interviews and step into real project roles with confidence.
Our Students Work At
For Quick Questions
Oracle Cloud Infra 2026 Videos
Get Course Full Syllabus
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Training Details
Introduction To Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Training
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is a powerful enterprise cloud platform that enables organizations to run secure, scalable, and high-performance computing workloads directly on Oracle Cloud. It provides core infrastructure services such as compute, storage, networking, databases, and security to support modern cloud-native and enterprise applications.
It empowers businesses to migrate on-premise systems, build cloud architectures, deploy mission-critical applications, and manage resources efficiently using integrated automation, monitoring, and security services.
OCI cloud professionals play a critical role in digital transformation — designing resilient cloud environments, optimising performance, ensuring security compliance, and supporting enterprise workloads across industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and IT services.
Key Features & Capabilities
- Enterprise Cloud Architecture – Design scalable, high-performance OCI environments
- Core Infrastructure Services – Compute, Storage, Networking & Load Balancing
- Identity & Security Management – IAM policies, compartments & resource governance
- Database & Autonomous Services – OCI DB systems & autonomous database deployment
- High Availability & Disaster Recovery – Multi-region architecture & fault domains
- Cost Management & Monitoring – Budgeting, tagging & resource optimization
- Cloud Migration Strategy – Lift-and-shift EBS, JDE & on-premise workloads
Become a Certified Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Consultant
Looking to build a high-paying career as an OCI Architect or Cloud Engineer?
Join UnoGeeks’ Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Online Training Program — trusted by professionals and recognized as a leading Oracle training institute.
We focus on real-time cloud deployments, certification preparation (Associate & Professional), enterprise architecture design, and hands-on infrastructure projects.
What You Will Learn
- Master all OCI concepts required for Architect Associate & Professional certification exams
- Learn cloud computing fundamentals and OCI architecture hands-on from industry expert
- Configure OCI core services including IAM, Compute, Storage, VCN, Load Balancer & Security
- Design real-time enterprise cloud networking architectures
- Deploy applications on OCI for real-world business scenarios
- Migrate on-premise applications (EBS, JDE, legacy systems) to Oracle Cloud
- Implement Messaging, Notifications, Resource Manager & Cost Governance
- Build secure multi-tier cloud environments with high availability
- Hands-on real-time project scenarios
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure certification guidance and exam preparation
- Resume building + mock interviews with personalised feedback
- Job readiness support with regular OCI job openings and referrals
🔔 Daily Oracle Job Alerts by UnoGeeks
Follow us on LinkedIn for real hiring updates: 👉 UnoGeeks OCI LinkedIn Jobs
Who Can Enrol in This Course?
- IT professionals looking to transition into cloud infrastructure roles
- System administrators & network engineers moving to OCI
- Developers wanting to learn cloud architecture
- Graduates & freshers starting cloud careers
Prerequisites
No prior Oracle Cloud experience required.
We cover foundational concepts as part of the training, including:
- Basics of Cloud Computing
- Virtualisation & Infrastructure concepts
- Networking fundamentals
- Security fundamentals
Register for a Free Demo
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Training Course Curriculum
- What is Cloud Computing
- Service Models
- High Availability
- Disaster Recovery
- Cloud Terminology
- How Cloud Computing converts CAPITAL EXPENDITURE to OPERATIONAL EXPENDITURE?
- Why OCI?
- OCI Global Footprint
- OCI Architecture – Regions, Availability Domains (AD) and Fault Domains (FD)
- OCI Regions with one AD regions
- What factors to consider while choosing a region?
- How to avoid single points of failure?
- How to design High Availability, Scale and Performance Network with in AD
- OCI Services Overview
- High level overview of the course content
- Oracle Cloud Account Sign Up Process for Free Tier Account
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console Overview
- Identity and Access Management Principals, Users and Groups
- Authentication and Authorization in IAM
- IAM Policies, Policy Syntax and Verbs & Permissions
- IAM Common and Advanced Policies & Advanced Policy Syntax
- IAM Compartments, Policy Inheritance and Attachment for Compartments
- Moving Compartments and Policy Implications to consider while moving Compartments
- Understand how to use Tags and Audit Service effectively
- Introduction to Networking Concepts
- CIDR Basics
- Introduction to Virtual Cloud Network
- IP Address range for VCN, Public and Private IP Addresses
- Subnets, Gateways and Route Tables
- Internet, NAT, Service, Dynamic Gateways
- Peering, Local and Remote Peering
- Transit Routing, Hub and Spoke & private access
- Security List (SL) and Network Security Group (NSG)
- Stateful and Stateless Security Rules
- Virtual Cloud Network Summary
- Introduction to OCI Compute Service
- Bare Metal, VM and Dedicated Hosts
- Machine Images, Custom Images and Oracle Provided Images
- Image Import/Export, Bring your own Image (BYOI)
- Custom Boot Volume, Custom Image versus Boot Volume Backup
- Instance Configurations, Pools, Autoscaling
- Autoscaling Configurations
- Instance Lifecycle and Metadata
- OCI Compute Service Summary
- Introduction to OCI Load Balancing Service
- Public and Private Load Balancer
- Regional Subnets and AD Specific Subnets
- Load Balancing Policies and Health Checks
- Introduction to OCI Storage Services
- Use cases for Object Storage usage
- Object Naming, Object Storage Tiers and Capabilities
- Object Storage Access and Authentication
- Object lifecycle management
- Introduction to OCI Storage Services
- Block Volume Service
- Creating and Attaching Block Volumes
- Detaching and Deleting Block Volumes
- Block Volume Resize, Back Up and Restoration
- Clone, Volume Groups & Boot Volumes
- Introduction to OCI Storage Services
- File Storage Service Use Cases
- File Storage service Features
- Mount Target
- File System, FSS Paths, Mounting an OCI File System
- File Storage Service Security
- Security Lists, Export Option and Snapshots
- Introduction to OCI Database Service
- Virtual Machine (VM) Database (DB) Systems
- DB Systems – VM, BM, Exadata
- Database Editions, Versions and Options
- Managing & Patching DB Systems
- Automatic Backup and Restore
- High Availability and Scalability
- Oracle Data Guard
- Introduction to OCI Database Service
- Getting Started with Autonomous Database
- Autonomous Database Options
- Autonomous Database Cloud Deployment Options
- Autonomous Data Warehouse: Architecture
- Autonomous Transaction Processing: Architecture
- Auto Scaling & Securing Autonomous Database (ADB)
- Autonomous Database Cloud – Cloning
- Introduction to High Availability Concepts
- Availability Domains & Fault Domains
- Avoid Single Points-of-Failure
- Regional and AD Specific Subnets
- High Availability for OCI: Connectivity
- Configure Load Balancer for High Availability
- Create and Access OCI Budgets
- Set up Budgets Alert Emails
- Accessing Usage Reports
- Service Limits and Usage
- Compartment Quotas
- Quota Policies with Examples
- Cost Management Best Practices
- Different Ways to Access OCI
- Developer Tools with OCI
- Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Software Development Tool Kits (SDKs)
- Installing & Configuring Oracle Cloud Infrastructure CLI
- Working with OCI Services with CLI - Check Connectivity
- Downloading and Configuring SDKs for OCI
- Introduction to OCI Database Cloud Backup Service
- Backups via Cloud Tooling (Automatic and Manual)
- Command Line Tools (dbcli / bkup_api / dbaascli)
- Manual RMAN Backups
- Introduction to OCI Monitoring Service
- Metrics, Metric Queries & Alarms
- Use cases for OCI Monitoring Service
- Introduction to OCI Notification Service
- OCI Notifications Use Cases
- Why do I need tags?
- Tags Details & Tag Namespace
- Searching and Securing Tags
- Automating Tag Application
- Working with Defined Tags and Policies
- Create VCN
- Launch Compute Instance
- Install Apache Web Server
- Launch and access web server
- Create a Virtual Cloud Network
- Create Two Compute Instances and Install the Web Server
- Create Security List, Route table, and Additional Subnet
- Create Load Balancer and Update Security List
- Verify High Availability of HTTP Servers
- Delete the Resources
- Generate SSH Keys
- Create VCN
- Create Load Balancer and Update Security List
- Configure instance pool and auto scaling
- Test the Autoscaling setups
- Setup EBS Cloud Manager Authentication with Identity Cloud Service (IDCS)
- Create the EBS Cloud Manager Administrators group and user in IDCS
- Register Oracle E-Business Suite Cloud Manager as a Confidential Application in IDCS
- Deploy and Configure Oracle E-Business Suite Cloud Manager
- Provision an EBS Environment Using One-Click Provisioning
- Enable and Set Oracle E-Business Suite Account Passwords
- Open Firewall and Security List to Allow Connections to EBS Environment
- Configure Local Hosts File and Log in to Oracle E-Business Suite
- Data Safe
- OCI Auditing in an Autonomous Database
- Oracle Active Data Guard
- OCI Audit Service
- Explain certification options available in OCI
- Provide tips on how to clear for OCI Architect Associate & Professional Certification
- Help with Resume Preparation as OCI Infrastructure Specialist
- Discuss common interview questions in OCI
🎥 Watch How We Teach Oracle Cloud
🎓 Learn From Our Most-Watched real-time Oracle Cloud Sessions
For Quick Questions
Oracle Cloud Infra 2026 Videos
Get Course Full Syllabus
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Lead Trainer – Industry Expert for OCI Training at UnoGeeks

100+ Live Batches Delivered
2000+ Professionals Trained
15+ Years Oracle Technical Experience
Mr. Hemanth is the Lead OCI Trainer at UnoGeeks, with over 15+ years of real-world experience working as an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Architect at top US-based product companies.
He specialises in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) training, helping professionals gain hands-on expertise in cloud architecture design, compute and storage services, virtual cloud networking (VCN), identity and access management (IAM), load balancing, security best practices, database deployments, high-availability setups, and real-time enterprise cloud migrations used in live production environments.
Having trained professionals across India, the US, and global markets, Mr.Hemanth focuses on practical, implementation-driven learning rather than theoretical cloud concepts. His structured, step-by-step approach ensures learners become job-ready OCI consultants and cloud architects, capable of designing enterprise cloud infrastructures, migrating on-premise workloads, managing secure environments, and cracking OCI certification and cloud architecture interviews with confidence.
Earn Your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Certification with Confidence
Showcase your expertise with an official certificate recognized by employers.

UnoGeeks Sample Certificate
🎓 Official Certification
Earn an official course completion certificate validating your practical Oracle Cloud Infrastructure expertise
🔗 Oracle Certification
Our training will help you Become a Certified OCI Architect Associate & Professional
🌍 Industry Recognition
Strengthen your resume with widely recognized credential trusted by employers & consulting firms.
🚀 Career Advancement
Gain hands-on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure skills that help you stand out & advance in your career
Few Success Stories from Our Students ✅
✅ “Recent real placements & live student messages (updated regularly)”

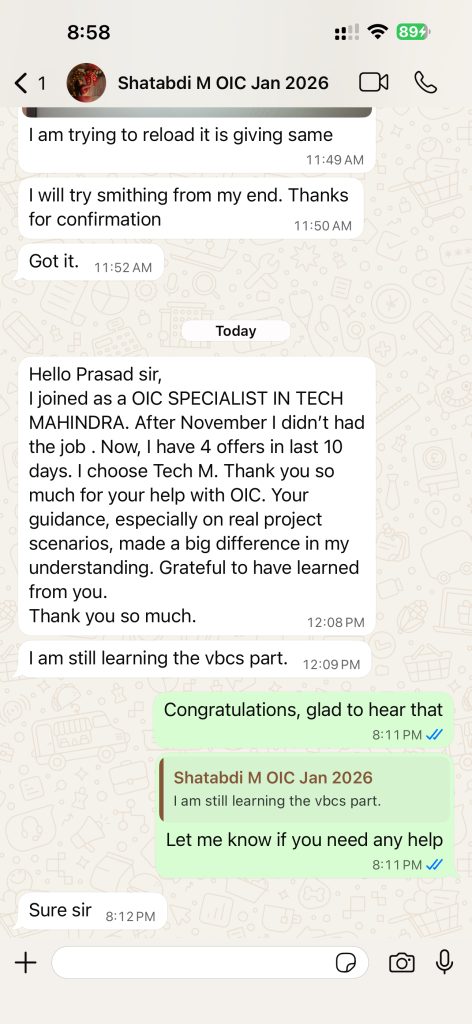

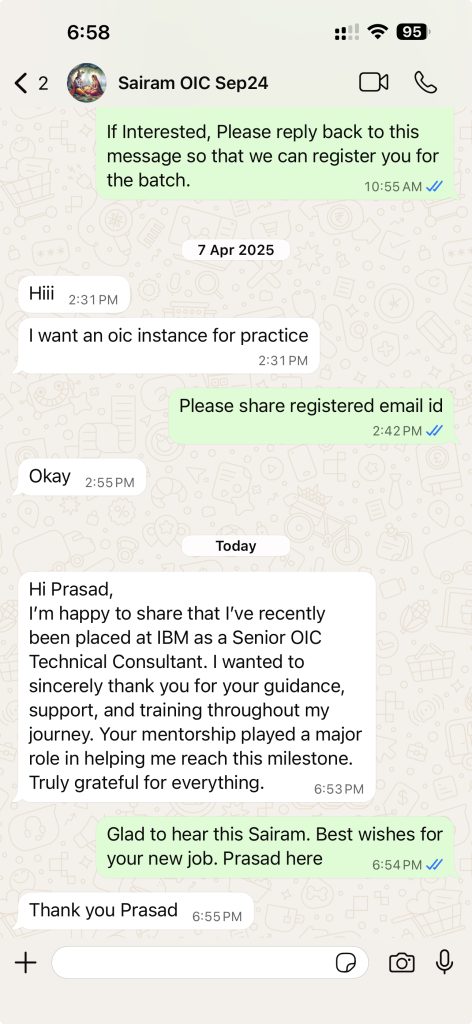

Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Consultant Jobs & Salary Trends
📈 High Market Demand
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure skills are in strong demand as enterprises rapidly migrate on-premise workloads, databases, and enterprise applications to Oracle Cloud. Organizations are actively hiring OCI cloud engineers and architects to design scalable infrastructure, manage secure cloud environments, implement networking and storage solutions, and support mission-critical systems—creating thousands of job opportunities across consulting firms and global enterprises.
🏢 Used by Global Firms
Leading organizations across IT, finance, healthcare, manufacturing, telecom, and retail rely on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure to run high-performance workloads and critical business operations. OCI consultants play a key role in designing cloud architectures, implementing security frameworks, managing large-scale deployments, and optimizing cloud performance at enterprise scale.
💰 Attractive Salaries
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure professionals earn highly competitive salaries worldwide, driven by strong demand for certified cloud engineers and architects with hands-on project experience. Freshers secure strong entry-level roles, while experienced OCI consultants consistently command premium compensation packages across top consulting firms and MNCs.
Our Training Advantage

Learn from Certified Experts
Get trained by industry-certified professionals with deep real-world Oracle Cloud implementation experience

Real-Time Implementation Projects
Learn through real project scenarios that mirror actual client implementations & production use cases.

Interactive Live Training Sessions
Highly interactive live sessions with recordings provided, so you never miss a concept or discussion.

Resume, Interview & Job Assistance
Guidance on resume building, interview preparation, and job support tailored to Oracle Cloud roles

Live Demos Before Enrolment
Attend up to 3 live demo sessions to evaluate the trainer, content quality, and teaching approach

24×7 Learning Support
Prompt support for queries, doubts, and technical issues throughout your learning journey.
What Students Say on Google
⭐ Rated 4.8★ by 600+ Google Reviews
Trusted by hundreds of professionals across Oracle Cloud domains
Free Career Call – Talk to Our Training Experts
Get batch details, syllabus, demo schedule, and fee structure — no obligation
+91 73960 33555
Get Batch Dates, Fees & Demo Details
+91 73960 33555
Mon–Sat | 6 AM – 10 PM IST
info@unogeeks.com
For detailed queries
Live Chat
Chat with our support team now
Trusted by 5,000+ learners | 500+ real-time batches completed
Why Students Trust UnoGeeks
500+
Real-Time Batches Completed
5000+
Happy Students
5 *****
Star Ratings
20+
Expert Trainers
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Training 2026 Batch Slots
WeekDay Batch 1
Monday – Friday

07:00 – 08:00 AM (IST)
WeekDay Batch 2
Monday – Friday

08:15 – 9:15 AM (IST)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Training 2026 FAQs
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure training teaches you how to design, deploy, and manage cloud environments using Oracle’s enterprise-grade IaaS platform. It covers core services such as compute, networking, storage, identity management, databases, security, and high-availability architecture required for real-world OCI projects.
Yes. OCI training is beginner-friendly, especially if you have basic IT knowledge. Most programs start with cloud computing fundamentals before moving into Oracle Cloud Infrastructure architecture, core services, and hands-on deployments.
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure course typically includes cloud fundamentals, IAM policies, VCN networking, compute instances, storage services, load balancing, database services, monitoring, cost management, and real-time cloud deployment scenarios.
The best way to learn Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is through hands-on practice. A structured OCI training program with live cloud deployments, architectural design exercises, and certification preparation helps you become job-ready faster.
The OCI Architect Associate certification validates foundational knowledge in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure architecture, networking, security, compute, and storage services. It is ideal for beginners starting their cloud career.
The OCI Architect Professional certification is an advanced-level certification that demonstrates expertise in designing enterprise-grade cloud architectures, implementing high availability, disaster recovery, and secure OCI deployments.
Yes. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure certification increases credibility, improves job opportunities, and helps professionals secure better salary packages in cloud engineering and architecture roles.
After OCI training, you can work as an OCI Architect, Cloud Engineer, Cloud Infrastructure Consultant, DevOps Engineer (OCI-focused), or Oracle Cloud Administrator.
OCI professionals in India typically earn between ₹6 LPA and ₹20 LPA depending on experience, certification level, and project exposure. Certified architects with hands-on experience command higher compensation.
Yes. As enterprises migrate from on-premise systems to cloud environments, demand for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure engineers and architects continues to grow across consulting firms and multinational companies.
OCI foundation training covers cloud computing basics, Oracle Cloud regions and availability domains, identity and access management, networking fundamentals, storage types, compute models, and basic cloud security concepts.
Yes. Freshers can learn Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with structured training and guided hands-on practice. Basic understanding of networking and IT concepts is helpful but not mandatory.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure certification exam costs vary depending on level and region, but typically range between $95 to $245. Exact pricing is available on Oracle’s official certification portal.
Yes. OCI supports lift-and-shift migration of on-premise applications such as EBS, JD Edwards, legacy ERP systems, and enterprise workloads to Oracle Cloud with high performance and security.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is widely used across IT services, finance, healthcare, telecom, retail, manufacturing, and government sectors for secure and scalable cloud deployments.
OCI is known for strong database performance, enterprise-grade security, high availability, and competitive pricing models. It is especially preferred by organizations already using Oracle products.
OCI training includes Virtual Cloud Networks (VCN), subnets, route tables, internet gateways, NAT gateways, load balancers, security lists, and high-availability network architecture design.
Most Oracle Cloud Infrastructure training programs take 6–10 weeks depending on depth, certification preparation, and hands-on practice.
Real-time projects include deploying multi-tier applications, configuring IAM policies, designing VCN architecture, implementing load balancing, setting up high availability environments, and migrating enterprise applications to OCI.
UnoGeeks provides real-time, project-driven Oracle Cloud Infrastructure training focused on certification preparation, enterprise architecture design, cloud deployment practice, resume building, and mock interviews to ensure full job readiness.
